Kazakhstan in Brief
The Republic of Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan is a country with a rich historical past, a land of great opportunities, seeking to become one of the most competitive economies in the world.
The Republic of Kazakhstan is a unitary state with a presidential form of government.
Kazakhstan became an independent state on December 16, 1991. The capital is Astana city. The official language is Kazakh, while Russian has the status of a lingua franca. The currency unit is tenge.
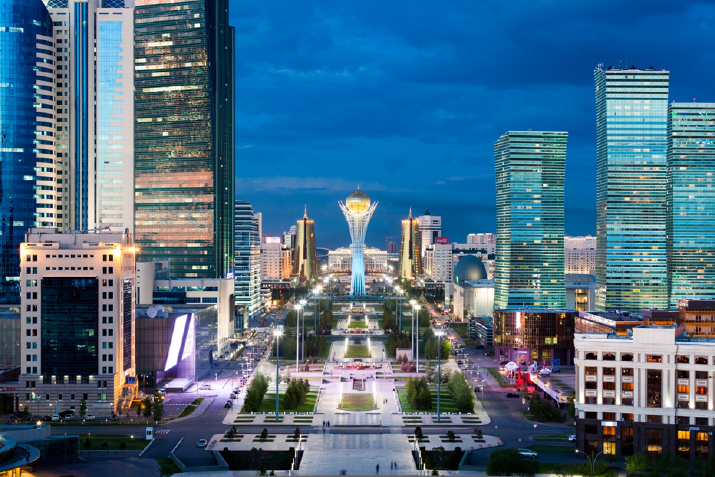

The government of Kazakhstan has three branches: the executive, the legislative, and the judicial.
The executive branch

- the Government of the Republic of Kazakhstan
The legislative branch

- the Parliament comprising the Senate (Upper House) and the Majilis (Lower House)
The judicial branch

- the Supreme Court and local court system
The country’s administrative and territorial structure consists of 17 regions and 3 cities of national significance, namely Astana, Almaty and Shymkent.
The Peoples of the Republic of Kazakhstan
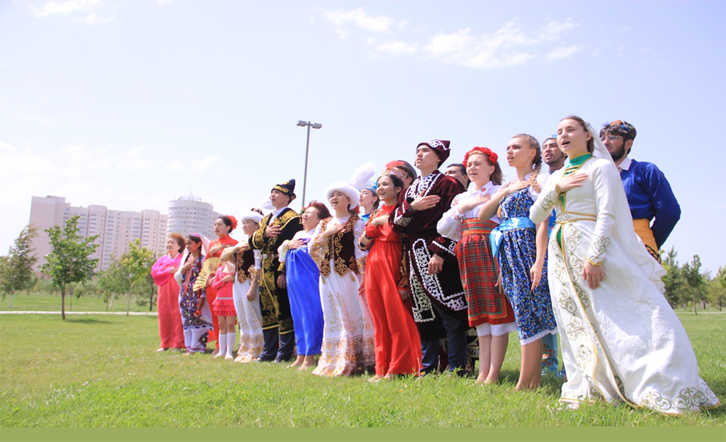

The population of Kazakhstan exceeds 20 million people. Kazakhstan is a multinational, secular country with a population comprising about 130 ethnic groups.
Population of Kazakhstan by ethnicity:
63.07%
23.7%
- Kazakhs - 70,4%
- Russians - 15,5%
- Uzbeks - 3,2%
- Ukrainians - 2%
- Uygurs - 1.5%
- Germans - 1,2%
- Tatars - 1,1%
- Others - 5,1%.
Kazakhstan on the world map
Kazakhstan is the largest landlocked country in the world. Deserts and semi-deserts make up most of the country's territory, comprising 44% and 14% respectively. Steppes occupy 26% of the territory, while forests cover 5.5%. Kazakhstan boasts 8.5 thousand rivers as well as 48 thousand large and small lakes. The largest lakes are Balkhash, Zaisan and Alakol. Kazakhstan has a continental climate.
Kazakhstan has a unique mineral resource base. The World Bank estimates that there are over 5000 unexplored deposits still present in Kazakhstan, valued at over 46 trillion dollars. Kazakhstan is first in the world in explored reserves of zinc, tungsten and barite, second in silver, lead and chromite, third in copper and fluorite, fourth in molybdenum and sixth in gold.
Kazakhstan also has significant oil and gas resources. The country is ranked ninth globally in proven oil reserves, which are concentrated in the western regions. Additionally, Kazakhstan ranks eighth in the world in coal reserves and second in uranium reserves.
Kazakhstan is also among the global top ten exporters of grain and one of the leading exporter of flour.

Exported goods are predominantly produced by the mining, fuel, power, metallurgical, chemical and grain industries. The main trade partners are Russia and other CIS countries, China and Europe.
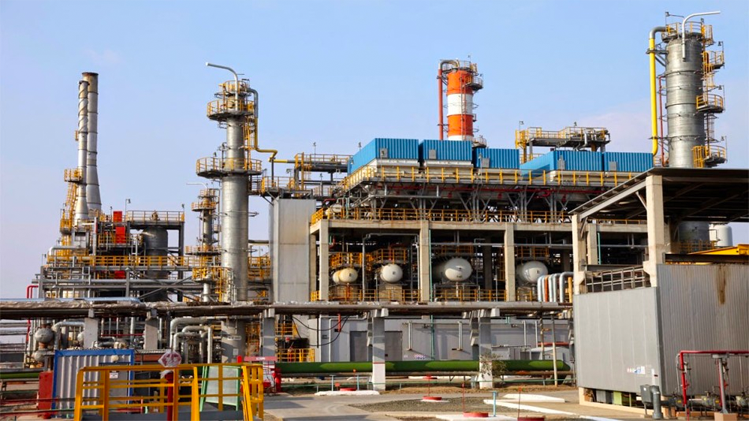

Pavlodar Petrochemical Plant
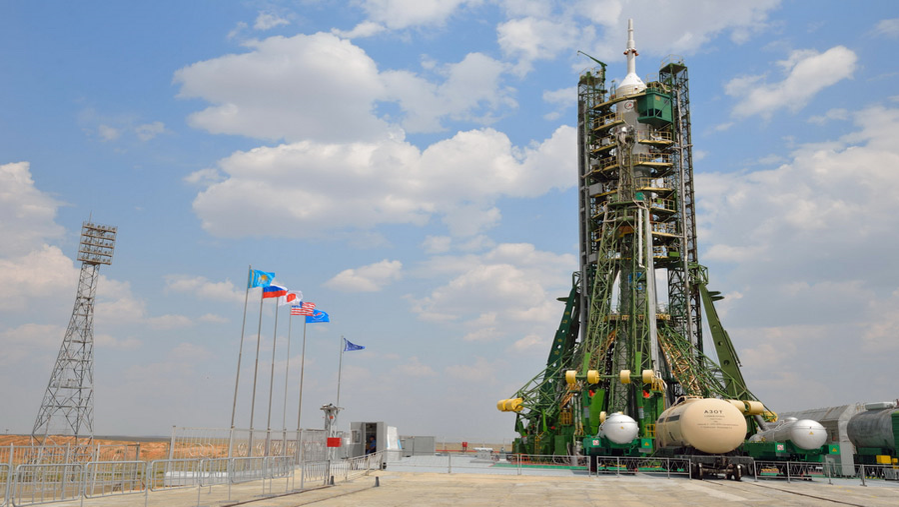
The Baikonur Cosmodrome, the world's first and largest space launch facility, is located in southern Kazakhstan and covers an area of 6.717 sq km. It was opened in 1957 upon completion of the first phase of construction works and the launch of the world's first intercontinental ballistic missile - the R-7. Over 30 years, the Baikonur Cosmodrome expanded, with the development of launch pads for new types of missiles, assembly workshops, fueling stations, complexes for missile management and monitoring, as well as other facilities and infrastructure. The main launch site at the Baikonur Cosmodrome is launch site No.1, commonly known as Gagarin's Start.

Stable growth of all economy sectors, political stability and international recognition became a basis for prosperity of Kazakhstan’s society.

























